Path: blob/main/transformers_doc/ko/image_captioning.ipynb
8386 views
이미지 캡셔닝[[image-captioning]]
이미지 캡셔닝(Image captioning)은 주어진 이미지에 대한 캡션을 예측하는 작업입니다. 이미지 캡셔닝은 시각 장애인이 다양한 상황을 탐색하는 데 도움을 줄 수 있도록 시각 장애인을 보조하는 등 실생활에서 흔히 활용됩니다. 따라서 이미지 캡셔닝은 이미지를 설명함으로써 사람들의 콘텐츠 접근성을 개선하는 데 도움이 됩니다.
이 가이드에서는 소개할 내용은 아래와 같습니다:
이미지 캡셔닝 모델을 파인튜닝합니다.
파인튜닝된 모델을 추론에 사용합니다.
시작하기 전에 필요한 모든 라이브러리가 설치되어 있는지 확인하세요:
Hugging Face 계정에 로그인하면 모델을 업로드하고 커뮤니티에 공유할 수 있습니다. 토큰을 입력하여 로그인하세요.
포켓몬 BLIP 캡션 데이터세트 가져오기[[load-the-pokmon-blip-captions-dataset]]
{이미지-캡션} 쌍으로 구성된 데이터세트를 가져오려면 🤗 Dataset 라이브러리를 사용합니다. PyTorch에서 자신만의 이미지 캡션 데이터세트를 만들려면 이 노트북을 참조하세요.
이 데이터세트는 image와 text라는 두 특성을 가지고 있습니다.
많은 이미지 캡션 데이터세트에는 이미지당 여러 개의 캡션이 포함되어 있습니다. 이러한 경우, 일반적으로 학습 중에 사용 가능한 캡션 중에서 무작위로 샘플을 추출합니다.
train_test_split 메소드를 사용하여 데이터세트의 학습 분할을 학습 및 테스트 세트로 나눕니다:
학습 세트의 샘플 몇 개를 시각화해 봅시다. Let's visualize a couple of samples from the training set.
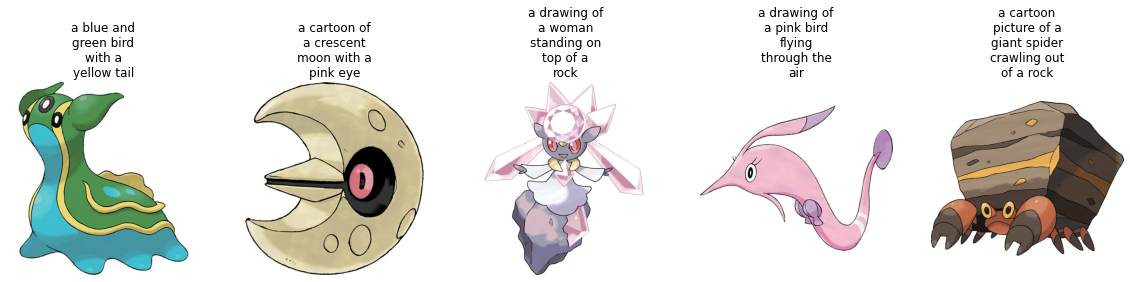
데이터세트 전처리[[preprocess-the-dataset]]
데이터세트에는 이미지와 텍스트라는 두 가지 양식이 있기 때문에, 전처리 파이프라인에서 이미지와 캡션을 모두 전처리합니다.
전처리 작업을 위해, 파인튜닝하려는 모델에 연결된 프로세서 클래스를 가져옵니다.
프로세서는 내부적으로 크기 조정 및 픽셀 크기 조정을 포함한 이미지 전처리를 수행하고 캡션을 토큰화합니다.
데이터세트가 준비되었으니 이제 파인튜닝을 위해 모델을 설정할 수 있습니다.
기본 모델 가져오기[[load-a-base-model]]
"microsoft/git-base"를 AutoModelForCausalLM 객체로 가져옵니다.
평가[[evaluate]]
이미지 캡션 모델은 일반적으로 Rouge 점수 또는 단어 오류율(Word Error Rate)로 평가합니다. 이 가이드에서는 단어 오류율(WER)을 사용합니다.
이를 위해 🤗 Evaluate 라이브러리를 사용합니다. WER의 잠재적 제한 사항 및 기타 문제점은 이 가이드를 참조하세요.
학습![[train!]]
이제 모델 파인튜닝을 시작할 준비가 되었습니다. 이를 위해 🤗 Trainer를 사용합니다.
먼저, TrainingArguments를 사용하여 학습 인수를 정의합니다.
학습 인수를 데이터세트, 모델과 함께 🤗 Trainer에 전달합니다.
학습이 진행되면서 학습 손실이 원활하게 감소하는 것을 볼 수 있습니다.
학습이 완료되면 모든 사람이 모델을 사용할 수 있도록 push_to_hub() 메소드를 사용하여 모델을 허브에 공유하세요:
추론[[inference]]
test_ds에서 샘플 이미지를 가져와 모델을 테스트합니다.
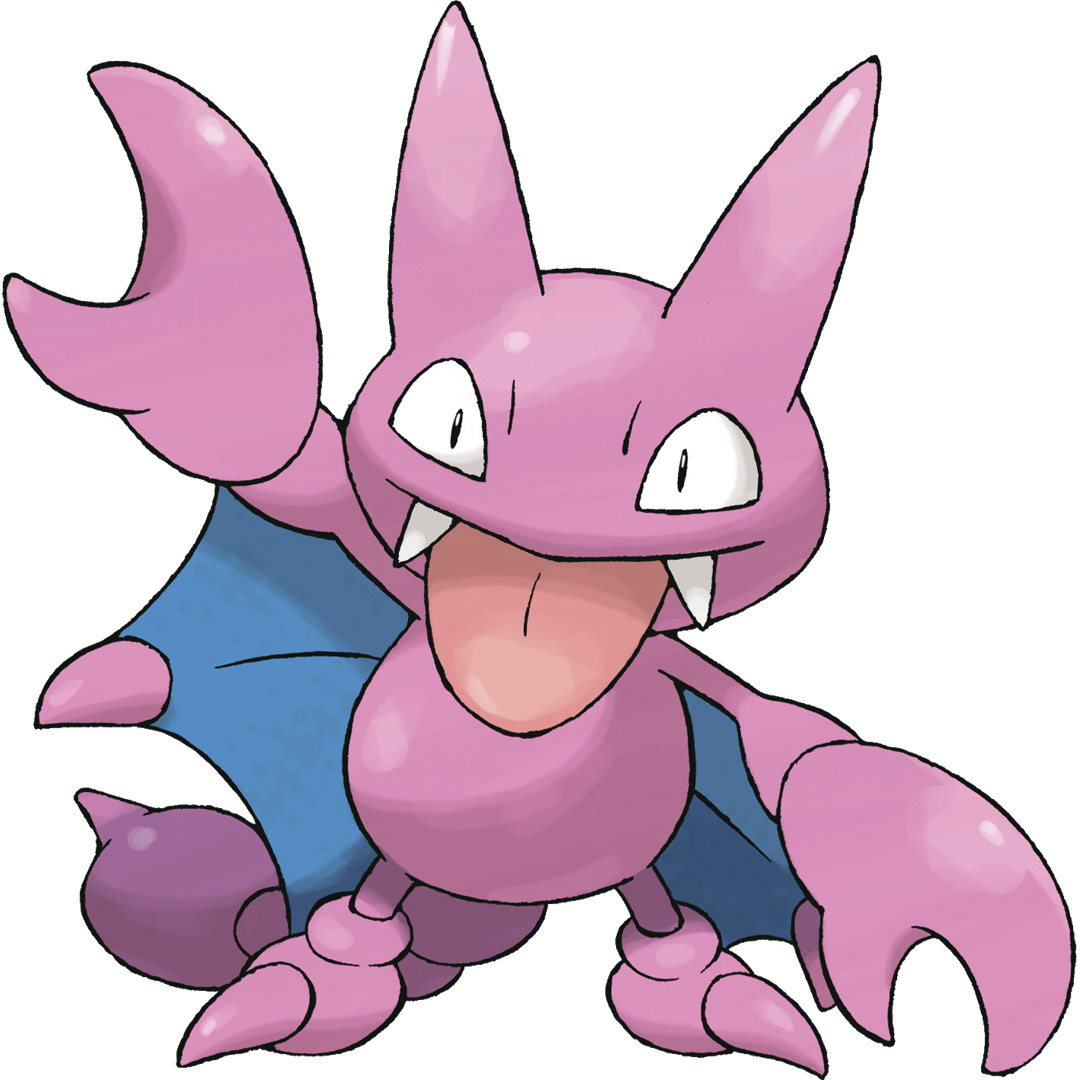

모델에 사용할 이미지를 준비합니다.
generate를 호출하고 예측을 디코딩합니다.
파인튜닝된 모델이 꽤 괜찮은 캡션을 생성한 것 같습니다!