Path: blob/master/site/ja/addons/tutorials/losses_triplet.ipynb
39072 views
Kernel: Python 3
Copyright 2020 The TensorFlow Authors.
In [ ]:
TensorFlow Addons 損失 : TripletSemiHardLoss
概要
このノートブックでは、TensorFlow Addons で TripletSemiHardLoss を使用する方法を紹介します。
リソース:
トリプレット損失
FaceNet の論文で初めて紹介されたトリプレット損失 (TripletLoss) は、異なるクラスの埋め込み間の距離を最大化しながら、同じクラスの特徴を密接に埋め込むようにニューラルネットワークをトレーニングする損失関数です。 これを行うために、1 つのネガティブサンプルと 1 つのポジティブサンプルと共にアンカーが選択されます。
損失関数はユークリッド距離関数として記述されます。
Oliver Moindrot のブログでは、アルゴリズムがとてもよく詳説されています
ここで、A はアンカー入力、P はポジティブサンプル入力、N はネガティブサンプル入力、およびアルファは、トリプレットが「簡単」になり過ぎて重みを調整する必要がなくなった時に指定するマージンです。
セミハードオンライン学習
論文にあるように、最良の結果は「セミハード」として知られるトリプレットから得られます。これらはネガティブがポジティブよりアンカーから離れていても、ポジティブの損失を生成するトリプレットと定義されています。これらのトリプレットを効率的に見つけるために、オンライン学習を利用して、各バッチのセミハードの例のみからトレーニングします。
セットアップ
In [ ]:
In [ ]:
In [ ]:
データを準備する
In [ ]:
モデルを構築する
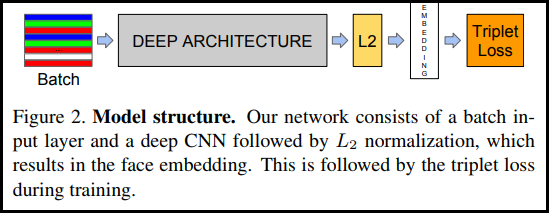
In [ ]:
トレーニングして評価する
In [ ]:
In [ ]:
In [ ]:
In [ ]:
プロジェクターを埋め込む
ベクトルファイルとメタデータファイルは、次のリンクから読み込んで可視化することができます。https://projector.tensorflow.org/
埋め込んだテストデータを UMAP で可視化すると、その結果を見ることができます。 
 TensorFlow.org で表示
TensorFlow.org で表示 Google Colab で実行
Google Colab で実行 GitHub でソースを表示
GitHub でソースを表示 ノートブックをダウンロード
ノートブックをダウンロード