Path: blob/master/site/ko/addons/tutorials/losses_triplet.ipynb
39061 views
Kernel: Python 3
Copyright 2020 The TensorFlow Authors.
In [ ]:
TensorFlow 애드온 손실: TripletSemiHardLoss
개요
이 노트북은 TensorFlow 애드온에서 TripletSemiHardLoss 함수를 사용하는 방법을 보여줍니다.
리소스:
TripletLoss
FaceNet 논문에 처음 소개된 TripletLoss는 신경망을 훈련하여 같은 클래스의 특성을 밀접하게 포함하면서 서로 다른 클래스의 임베딩 간의 거리를 최대화합니다. 이를 위해 하나의 음수 샘플과 하나의 양수 샘플과 함께 앵커가 선택됩니다. 
손실 함수는 Euclidean 거리 함수로 설명됩니다.

여기서 A는 앵커 입력, P는 양수 샘플 입력, N은 음수 샘플 입력, 알파는 삼중항이 너무 "쉽게" 되어 더 이상 가중치를 조정하고 싶지 않을 때 지정하는 데 사용하는 일부 여백입니다. .
SemiHard 온라인 학습
이 논문에서 볼 수 있듯이 가장 좋은 결과는 "Semi-Hard"로 알려진 트리플릿에서 얻습니다. 트리플릿은 음이 양보다 앵커에서 더 멀리 있는 트리플릿으로 정의되지만, 여전히 양의 손실을 생성합니다. 이러한 트리플릿을 효율적으로 찾기 위해 온라인 학습을 활용하고 각 배치에서 Semi-Hard 예제를 통해서만 훈련합니다.
설정
In [ ]:
In [ ]:
In [ ]:
데이터 준비하기
In [ ]:
모델 빌드하기
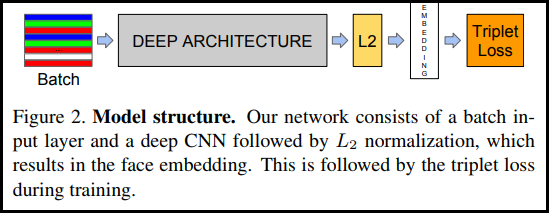
In [ ]:
훈련 및 평가하기
In [ ]:
In [ ]:
In [ ]:
In [ ]:
Embedding Projector
벡터 및 메타 데이터 파일은 https://projector.tensorflow.org/에서 로드하고 시각화할 수 있습니다.
UMAP으로 시각화하면 포함된 테스트 데이터의 결과를 볼 수 있습니다. 
 TensorFlow.org에서 보기
TensorFlow.org에서 보기 Google Colab에서 실행하기
Google Colab에서 실행하기 GitHub에서 소스 보기
GitHub에서 소스 보기 노트북 다운로드하기
노트북 다운로드하기