Path: blob/master/site/zh-cn/tutorials/text/nmt_with_attention.ipynb
39033 views
Copyright 2019 The TensorFlow Authors.
基于注意力的神经机器翻译
Note: 我们的 TensorFlow 社区翻译了这些文档。因为社区翻译是尽力而为, 所以无法保证它们是最准确的,并且反映了最新的 官方英文文档。如果您有改进此翻译的建议, 请提交 pull request 到 tensorflow/docs GitHub 仓库。要志愿地撰写或者审核译文,请加入 [email protected] Google Group。
此笔记本训练一个将西班牙语翻译为英语的序列到序列(sequence to sequence,简写为 seq2seq)模型。此例子难度较高,需要对序列到序列模型的知识有一定了解。
训练完此笔记本中的模型后,你将能够输入一个西班牙语句子,例如 "¿todavia estan en casa?",并返回其英语翻译 "are you still at home?"
对于一个简单的例子来说,翻译质量令人满意。但是更有趣的可能是生成的注意力图:它显示在翻译过程中,输入句子的哪些部分受到了模型的注意。
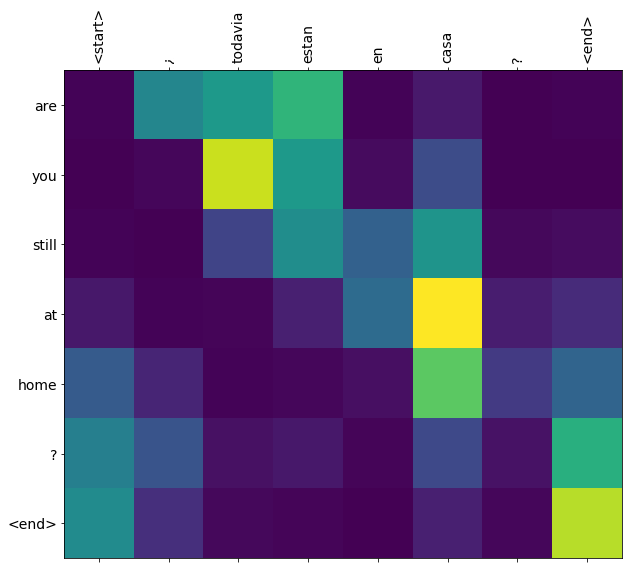
请注意:运行这个例子用一个 P100 GPU 需要花大约 10 分钟。
下载和准备数据集
我们将使用 http://www.manythings.org/anki/ 提供的一个语言数据集。这个数据集包含如下格式的语言翻译对:
这个数据集中有很多种语言可供选择。我们将使用英语 - 西班牙语数据集。为方便使用,我们在谷歌云上提供了此数据集的一份副本。但是你也可以自己下载副本。下载完数据集后,我们将采取下列步骤准备数据:
给每个句子添加一个 开始 和一个 结束 标记(token)。
删除特殊字符以清理句子。
创建一个单词索引和一个反向单词索引(即一个从单词映射至 id 的词典和一个从 id 映射至单词的词典)。
将每个句子填充(pad)到最大长度。
限制数据集的大小以加快实验速度(可选)
在超过 10 万个句子的完整数据集上训练需要很长时间。为了更快地训练,我们可以将数据集的大小限制为 3 万个句子(当然,翻译质量也会随着数据的减少而降低):
创建一个 tf.data 数据集
编写编码器 (encoder) 和解码器 (decoder) 模型
实现一个基于注意力的编码器 - 解码器模型。关于这种模型,你可以阅读 TensorFlow 的 神经机器翻译 (序列到序列) 教程。本示例采用一组更新的 API。此笔记本实现了上述序列到序列教程中的 注意力方程式。下图显示了注意力机制为每个输入单词分配一个权重,然后解码器将这个权重用于预测句子中的下一个单词。下图和公式是 Luong 的论文中注意力机制的一个例子。

输入经过编码器模型,编码器模型为我们提供形状为 (批大小,最大长度,隐藏层大小) 的编码器输出和形状为 (批大小,隐藏层大小) 的编码器隐藏层状态。
下面是所实现的方程式:
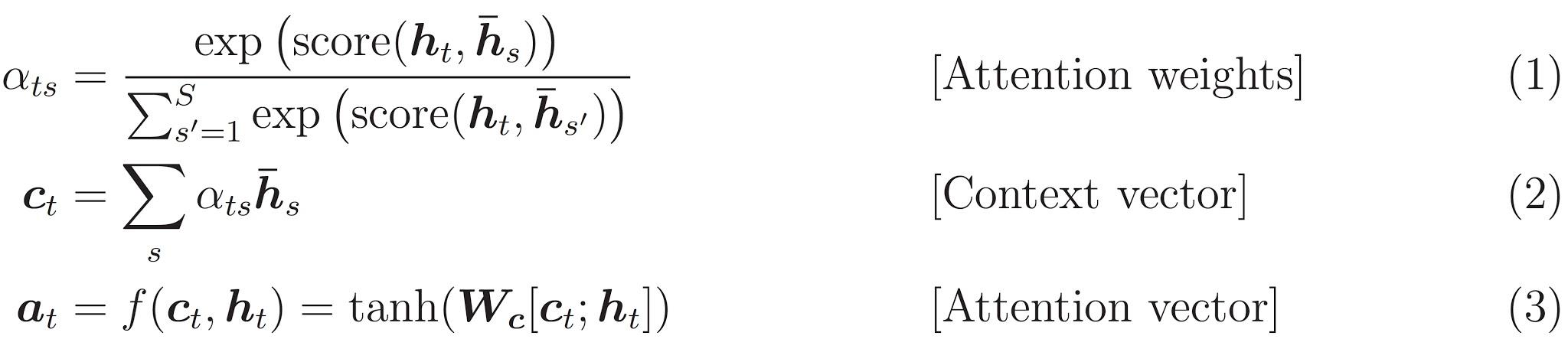
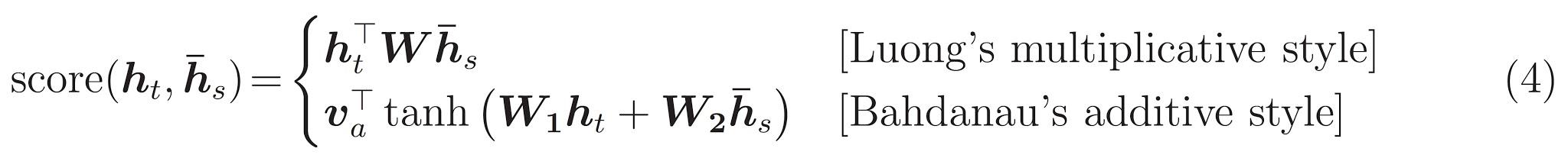
本教程的编码器采用 Bahdanau 注意力。在用简化形式编写之前,让我们先决定符号:
FC = 完全连接(密集)层
EO = 编码器输出
H = 隐藏层状态
X = 解码器输入
以及伪代码:
score = FC(tanh(FC(EO) + FC(H)))attention weights = softmax(score, axis = 1)。 Softmax 默认被应用于最后一个轴,但是这里我们想将它应用于 第一个轴, 因为分数 (score) 的形状是 (批大小,最大长度,隐藏层大小)。最大长度 (max_length) 是我们的输入的长度。因为我们想为每个输入分配一个权重,所以 softmax 应该用在这个轴上。context vector = sum(attention weights * EO, axis = 1)。选择第一个轴的原因同上。embedding output= 解码器输入 X 通过一个嵌入层。merged vector = concat(embedding output, context vector)此合并后的向量随后被传送到 GRU
每个步骤中所有向量的形状已在代码的注释中阐明:
定义优化器和损失函数
检查点(基于对象保存)
训练
将 输入 传送至 编码器,编码器返回 编码器输出 和 编码器隐藏层状态。
将编码器输出、编码器隐藏层状态和解码器输入(即 开始标记)传送至解码器。
解码器返回 预测 和 解码器隐藏层状态。
解码器隐藏层状态被传送回模型,预测被用于计算损失。
使用 教师强制 (teacher forcing) 决定解码器的下一个输入。
教师强制 是将 目标词 作为 下一个输入 传送至解码器的技术。
最后一步是计算梯度,并将其应用于优化器和反向传播。
翻译
评估函数类似于训练循环,不同之处在于在这里我们不使用 教师强制。每个时间步的解码器输入是其先前的预测、隐藏层状态和编码器输出。
当模型预测 结束标记 时停止预测。
存储 每个时间步的注意力权重。
请注意:对于一个输入,编码器输出仅计算一次。
恢复最新的检查点并验证
下一步
下载一个不同的数据集实验翻译,例如英语到德语或者英语到法语。
实验在更大的数据集上训练,或者增加训练周期。
 在 TensorFlow.org 上查看
在 TensorFlow.org 上查看 在 Google Colab 运行
在 Google Colab 运行 在 GitHub 上查看源代码
在 GitHub 上查看源代码 下载此 notebook
下载此 notebook